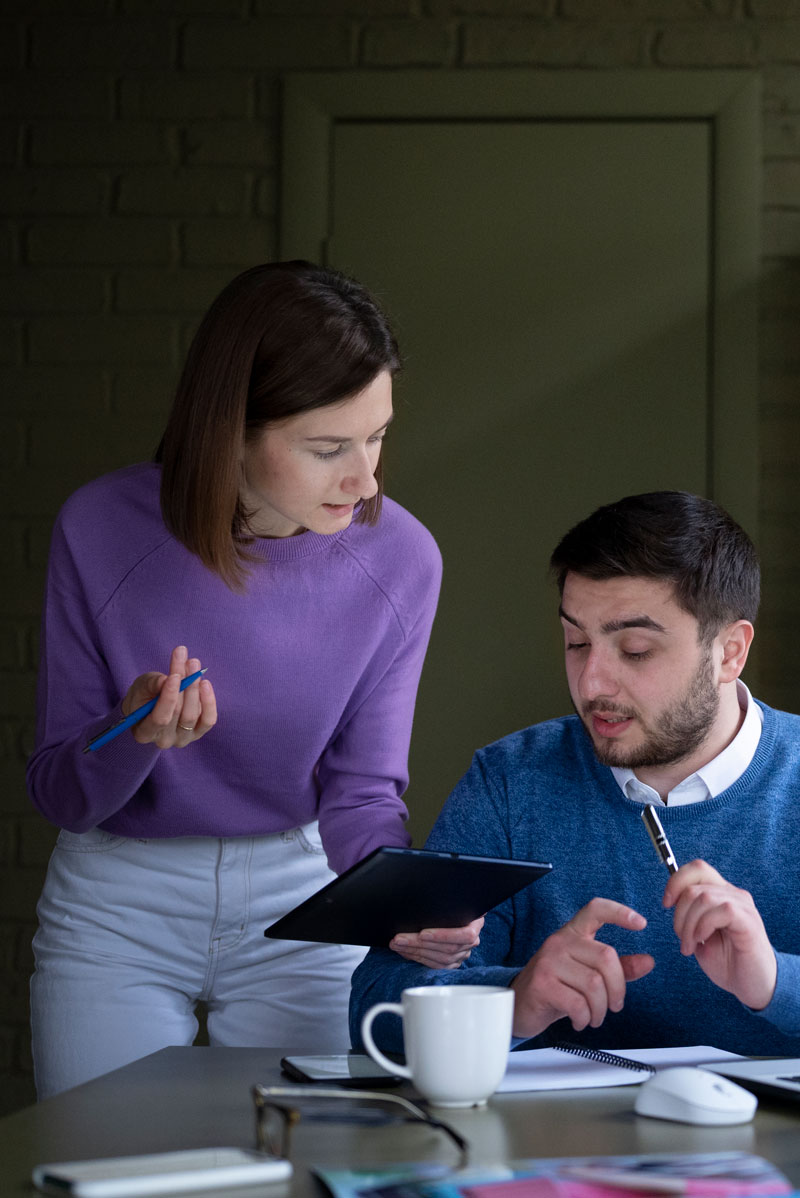


Welcome to our comprehensive loan guide, designed to help you navigate the complex world of loans and financial planning. Whether you're a first-time borrower or looking to expand your knowledge, this guide provides valuable insights into different types of loans, eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and application processes.
At Arav Digital Fincare, we believe that informed borrowers make better financial decisions. Our expert-curated guide aims to demystify loan concepts and empower you with the knowledge needed to choose the right loan product for your specific needs.
Loans come in various forms, each designed to serve specific financial needs. Understanding the different types can help you choose the right option for your particular situation.
Unsecured loans for personal expenses with no collateral requirement. Ideal for medical emergencies, travel, home renovation, or debt consolidation. Features quick approval, minimal documentation, and flexible usage.
Secured loans for purchasing, constructing, or renovating residential property. The property itself serves as collateral. Features long repayment tenures, competitive interest rates, and tax benefits.
Loans designed for business purposes like expansion, working capital, equipment purchase, or inventory management. Available as both secured and unsecured options based on loan amount and business profile.
Loans for funding higher education expenses including tuition fees, accommodation, books, and equipment. Features moratorium period during study, tax benefits, and flexible repayment options after course completion.
Secured loans where an existing property is mortgaged as collateral. Ideal for various financial needs like business expansion, education, or debt consolidation while retaining ownership of the property.
Secured loans for purchasing new or used vehicles. The vehicle itself serves as collateral. Features quick processing, competitive interest rates, and flexible repayment options tailored to budget constraints.
Understanding the terminology associated with loans can help you make informed decisions and avoid confusion during the loan process.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Principal | The original amount borrowed, excluding interest or additional charges. |
| Interest Rate | The percentage charged on the principal amount, determining the cost of borrowing. |
| EMI | Equated Monthly Installment - The fixed payment amount made by a borrower to a lender each month. |
| Tenure | The duration over which the loan must be repaid, typically expressed in months or years. |
| Collateral | Assets pledged by the borrower to secure a loan, which can be seized by the lender in case of default. |
| Processing Fee | A one-time charge levied by lenders to process the loan application, typically a percentage of the loan amount. |
| Foreclosure | The act of repaying the entire loan amount before the end of the tenure. |
| CIBIL Score | A three-digit numeric summary of a person's credit history, ranging from 300 to 900. |
| Amortization | The process of gradually reducing a debt through regular payments of principal and interest. |
| FOIR | Fixed Obligation to Income Ratio - The proportion of monthly income that goes toward loan repayments. |
| LTV Ratio | Loan-to-Value Ratio - The ratio between the loan amount and the market value of the asset being financed. |
| Moratorium Period | A temporary suspension of loan repayment, often granted for education loans during the study period. |
Understanding the fundamental difference between secured and unsecured loans can help you choose the right loan type based on your needs and circumstances.
Secured loans require collateral - an asset that the lender can claim if you fail to repay the loan. The collateral reduces the lender's risk, allowing for higher loan amounts, lower interest rates, and longer repayment periods.
Unsecured loans don't require collateral. Approval is based primarily on your credit history, income, and ability to repay. Since there's higher risk for lenders, these loans typically feature higher interest rates and stricter eligibility criteria.
Consider these factors when deciding between secured and unsecured loans:
For larger loan amounts (typically over ₹10 lakhs), secured loans are more suitable as they offer higher borrowing limits.
If getting the lowest possible interest rate is important to you, secured loans generally offer more competitive rates.
For longer repayment periods (over 5 years), secured loans typically offer more flexible tenure options.
Unsecured loans generally have faster processing and disbursement times compared to secured loans.
Consider whether you're comfortable with the risk of losing your collateral in case of payment difficulties.
If you have a lower credit score, secured loans might be more accessible as they pose less risk to lenders.
The type of interest rate you choose can significantly impact your loan repayment. Understanding the differences between fixed and floating rates is crucial for making an informed decision.
| Aspect | Fixed Interest Rate | Floating Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interest rate remains constant throughout the loan tenure | Interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions and changes in benchmark rates |
| Starting Rate | Usually higher than floating rate initially | Usually lower than fixed rate initially |
| EMI Pattern | Fixed EMIs throughout the loan tenure | EMIs can change when the interest rate changes |
| Risk Factor | Lower risk as you're protected from interest rate hikes | Higher risk as rates may increase, leading to higher EMIs |
| Benefit Factor | No benefit if market rates decrease | Benefits from decreasing market interest rates |
| Prepayment Charges | Often higher prepayment or foreclosure charges | Lower or no prepayment charges in many cases |
| Ideal For |
|
|
| Common Examples |
|
|
In a declining interest rate environment, floating rates may be more beneficial. In a rising interest rate scenario, fixed rates provide stability.
For long-term loans (over 10 years), the potential benefit of floating rates over time might outweigh short-term fluctuations.
If your income is stable and you have sufficient buffer, you might be able to handle the uncertainty of floating rates.
Some lenders offer hybrid loans where rates are fixed for an initial period and then converted to floating rates.
Understanding the eligibility requirements for different loans can help you assess your borrowing options and improve your chances of approval.
Most loans require borrowers to be between 21-65 years of age. The maximum age at loan maturity is typically 65-70 years for salaried individuals and up to 75 years for self-employed professionals.
Minimum income requirements vary by loan type and amount. Personal loans typically require ₹15,000-₹25,000 monthly income, while home loans may require ₹25,000-₹50,000 monthly income depending on the loan amount.
A credit score of 700+ is generally considered good. Higher scores improve loan approval chances and may secure better interest rates. Some loans have minimum score requirements (650-700).
For salaried individuals, most lenders require 2+ years of overall experience with 6-12 months at the current employer. Self-employed applicants typically need 2-3 years of business operation.
Lenders assess the proportion of income going toward debt repayments. Most lenders cap FOIR at 50-60%, meaning all EMIs (including the new loan) should not exceed this percentage of monthly income.
For home loans or mortgage loans, the property should have clear title, necessary approvals, and comply with local regulations. The property's value and condition impact the loan amount.
| Loan Type | Key Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|
| Personal Loan |
|
| Home Loan |
|
| Business Loan |
|
| Education Loan |
|
| Mortgage Loan |
|
Proper documentation is crucial for smooth loan processing. Here's a comprehensive guide to the documents required for different types of loans.
Ensure all documents are self-attested and clearly legible
Provide the most recent versions of all documents
Maintain consistency in personal details across all documents
Keep digital copies of all documents for easy reference
Submit complete documents at once to avoid processing delays
Have additional supporting documents ready if requested
Understanding the loan application process helps you prepare better and ensures a smoother experience from application to disbursement.
Research different loan options, interest rates, processing fees, and repayment terms. Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best fit for your requirements. Consider working with Arav Digital Fincare to simplify this process.
Gather all required documents based on the loan type and lender requirements. Ensuring you have complete and up-to-date documentation ready will help expedite the loan application process.
Submit your loan application along with all required documents. You can apply through Arav Digital Fincare, which will help you submit applications to multiple banks simultaneously, increasing your chances of approval.
The lender will verify your application, documents, credit history, and eligibility. This may include credit checks, income verification, property valuation (for secured loans), and possibly a personal interview.
If your application meets all criteria, the lender issues a loan approval letter or sanction letter. This document outlines the approved loan amount, interest rate, tenure, and other terms and conditions.
After accepting the loan offer, complete all legal formalities including signing the loan agreement, submitting post-dated cheques or setting up ECS mandates, and completing property documentation (for secured loans).
Once all formalities are completed, the loan amount is disbursed. For home loans or education loans, disbursement may be in installments based on construction progress or tuition payment schedule.
The final stages of the loan process involve important steps that borrowers should understand to ensure a smooth transition from approval to receiving funds.
When you receive a loan approval or sanction letter, it's crucial to understand every aspect of the offer before proceeding. Here are key elements to review:
If any terms differ from what was initially discussed or if certain conditions seem unclear, don't hesitate to seek clarification before proceeding.
The disbursement process varies based on loan type and purpose. Here are important aspects to consider:
Understanding various repayment options helps you manage your loan effectively and choose the most suitable approach for your financial situation.
Electronic Clearing Service or National Automated Clearing House allows automatic deduction of EMI from your bank account on the due date.
Providing a series of dated cheques in advance that the lender can deposit on respective due dates.
Manually paying your EMI through net banking, UPI, payment apps, or the lender's website/app.
Even with automated payments, set calendar reminders to ensure sufficient account balance before due dates.
Request EMI dates that align with your salary credit dates to ensure fund availability.
Maintain 3-6 months of EMI payments as an emergency buffer for financial contingencies.
Use bonuses or windfall gains to make partial prepayments and reduce overall interest burden.
For floating rate loans, stay updated on rate changes and understand how they affect your EMI or tenure.
Keep all payment receipts and loan statements for future reference and tax purposes.
Understanding the options for early loan repayment can help you save on interest costs and become debt-free sooner.
Partial prepayment involves paying an additional amount over and above your EMI to reduce the principal outstanding. This helps decrease the overall interest burden and can potentially reduce the loan tenure.
Foreclosure refers to completely paying off the remaining loan amount before the end of the tenure. This eliminates the debt entirely and frees you from future interest payments.
Many loans come with prepayment penalties, typically ranging from 2-5% of the prepaid amount. These charges can significantly impact the financial benefit of prepayment.
Lenders often have specific terms regarding prepayment that you should be aware of:
Consider the tax benefits you might lose after prepayment/foreclosure:
Before prepaying, compare the financial benefit against other options:
Review your loan agreement for prepayment terms and calculate the potential interest savings versus any applicable charges.
Inform your lender about your intention to prepay/foreclose and request the exact outstanding amount including any charges.
Fill out the prepayment/foreclosure request form provided by your lender, specifying whether it's partial prepayment or complete foreclosure.
Arrange for the payment through NEFT/RTGS, cheque, or as advised by your lender.
For foreclosure, collect no-dues certificate and request release of collateral documents (for secured loans).
Calculate how much you can save by making prepayments on your loan.
Our loan experts are available to guide you through the entire loan process, from application to disbursement. Contact us today for personalized assistance.
Refinancing or transferring your existing loan to another lender can help you secure better terms and save money on interest payments.
A balance transfer or refinancing involves moving your existing loan from one lender to another to take advantage of better terms such as lower interest rates, extended tenure, improved service, or additional top-up loan amounts.
When there's a difference of at least 0.5-1% between your current and the offered interest rate, especially for large loan amounts and long remaining tenures.
Most beneficial when at least 5-10 years of the loan tenure remain, as the interest component is higher in the initial years.
If your credit score has improved significantly since you took the original loan, you might qualify for better rates now.
When you need additional funds along with refinancing your existing loan through a top-up facility.
Consider all costs involved in the transfer process:
Calculate whether the potential savings outweigh the transfer costs:
Compare the new loan's terms with your existing loan:
Be prepared for the time involved in the transfer process:
Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best terms. Consider interest rates, fees, tenure options, and service quality.
Request a foreclosure letter or loan outstanding statement from your current lender, including remaining principal, interest, and any foreclosure charges.
Submit an application to the new lender along with required documents. Specify that it's a balance transfer application.
Complete documentation with the new lender after receiving approval. This includes loan agreement, security documents, and ECS/PDC setup.
The new lender transfers the outstanding amount to your existing lender to settle the loan. This is typically done directly between the lenders.
Collect the No-Dues Certificate and original property documents (for secured loans) from the previous lender and submit them to the new lender if required.
At Arav Digital Fincare, we can help you navigate the balance transfer process seamlessly, comparing offers from multiple banks to find the best option for your specific situation.
Explore Balance Transfer OptionsEven the most financially disciplined borrowers may face situations that affect their ability to make loan payments on time. Understanding how to manage payment difficulties can help protect your credit score and relationship with lenders.
A payment is considered delayed when it's not received by the due date specified in the loan agreement. Understanding the consequences of delays helps prioritize timely payments.
Being proactive about potential payment issues can help you avoid defaults and minimize their impact. Here are strategies to help manage your loan repayments effectively:
Create calendar alerts for payment due dates. Set these reminders 3-5 days before the actual due date to allow for processing time.
Set aside funds equivalent to 3-6 months of EMIs as an emergency buffer for financial contingencies.
Request your lender to set EMI due dates a few days after your salary credit date to ensure fund availability.
Set up auto-debit mandates (ECS/NACH) or standing instructions to ensure automatic EMI payments.
Enable SMS/email alerts for low balance notifications and for successful/failed EMI debits.
If you anticipate difficulty in making an upcoming payment, contact your lender immediately. Proactive communication shows responsibility and often leads to more accommodating solutions.
If your financial difficulty is expected to continue for some time, request for loan restructuring. This may involve modifying the loan terms to make repayments more manageable during the difficult period.
If you're facing difficulty due to high EMIs, explore balance transfer options to a lender offering lower interest rates or more flexible repayment terms.
Look into various sources of financial help that could provide temporary relief during difficult periods.
Respond to lender notices and calls promptly. Avoiding communication can escalate the situation and lead to more severe consequences, including legal action.
Even if you can't pay the full EMI, make partial payments to demonstrate good faith. This shows your intention to repay and may make the lender more willing to work with you.
For severely delinquent accounts, lenders might accept a one-time settlement for less than the full amount. This will still affect your credit score but can resolve the debt situation.
Consider consulting a financial counselor or debt management professional who can negotiate with lenders on your behalf and help develop a recovery plan.
After resolving the default, focus on rebuilding your credit score through timely payments on other loans, responsible credit card usage, and maintaining low credit utilization.
If you're facing difficulties with loan repayments, our team at Arav Digital Fincare can help you explore options and negotiate with lenders on your behalf. We're committed to helping you through challenging financial situations.
Get AssistanceDetermining how much you can responsibly borrow is crucial for maintaining financial health while meeting your funding needs.
Your borrowing capacity depends on several key factors that lenders evaluate to determine how much they can safely lend you. Understanding these factors helps you improve your borrowing potential.
Higher and more stable income translates to greater borrowing capacity. Lenders typically consider:
Most lenders cap the total EMIs (including the new loan) at 50-60% of your monthly income. Lower existing obligations mean higher borrowing capacity.
A good credit score (700+) and clean repayment history increase your borrowing capacity by demonstrating creditworthiness.
For secured loans, the value of the collateral significantly impacts borrowing capacity. For example, home loans typically offer 75-90% of property value.
Younger borrowers can get longer loan tenures, increasing borrowing capacity. Loans typically must be repaid before retirement age (usually 60-65 years).
Understanding how lenders calculate borrowing capacity can help you estimate how much you can borrow. Here are the primary methods used:
Many lenders use income multipliers to determine maximum loan amounts:
Formula: Maximum Loan Amount = Monthly Income × Income Multiplier
Example: If your monthly income is ₹50,000 and the income multiplier is 15, your maximum personal loan eligibility would be ₹7,50,000.
This method considers all existing loan EMIs and financial obligations:
Step 1: Calculate maximum allowable EMI
Maximum Monthly EMI = Monthly Income × Maximum FOIR (typically 50-60%) − Existing EMIs
Step 2: Calculate maximum loan amount using the EMI
Maximum Loan Amount = Maximum Monthly EMI × EMI Factor*
*EMI Factor varies based on interest rate and tenure. You can use EMI calculators for this step.
Example: If your monthly income is ₹80,000, FOIR limit is 50%, and existing EMIs are ₹15,000, your maximum allowable new EMI would be ₹25,000 (₹80,000 × 0.5 − ₹15,000).
For secured loans, lenders also consider the value of the collateral:
Formula: Maximum Loan Amount = Asset Value × Maximum LTV Ratio
Example: For a property valued at ₹1 crore with a maximum LTV of 80%, the maximum home loan amount would be ₹80 lakhs.
Note: The final loan amount would be the lower of the amounts calculated using the income method and the LTV method.
Increase your documented income by:
Lower your debt burden by:
Enhance your creditworthiness by:
Adjust loan parameters to enhance eligibility:
While understanding your maximum borrowing capacity is important, it's equally crucial to borrow only what you need and can comfortably repay. Consider these responsible borrowing principles:
Use our eligibility calculator to estimate your borrowing capacity based on your financial profile.
Comparing loan offers across multiple lenders helps you find the best terms for your specific needs. Here's how to effectively evaluate and compare loan options.
| Parameter | What to Look For | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate |
|
Even a small difference of 0.5% in interest rate can result in significant savings over the loan tenure. For a ₹50 lakh loan for 20 years, a 0.5% lower rate can save approximately ₹5-6 lakhs in total interest. |
| Processing Fee & Charges |
|
Upfront charges directly impact the effective cost of the loan. A loan with a slightly higher interest rate but no processing fee might be cheaper for shorter tenures. |
| Annual Percentage Rate (APR) |
|
APR provides a standardized way to compare the true cost of loans across lenders with different fee structures and interest rates. |
| Loan Tenure |
|
Longer tenures reduce EMI amount but increase total interest paid. The ability to choose from a range of tenure options allows customization based on repayment capacity. |
| Prepayment/Foreclosure Terms |
|
Favorable prepayment terms provide flexibility to reduce interest burden if you receive additional funds in the future. This is especially important for long-term loans. |
| Insurance Requirements |
|
Mandatory insurance adds to the overall loan cost. The freedom to choose your own insurance provider can often result in better coverage at lower premiums. |
| Turnaround Time |
|
Faster processing is crucial when time is of the essence, such as for business opportunities or time-bound property purchases. |
| Customer Service & Reputation |
|
Good service quality enhances the overall loan experience, especially for long-term loans where you'll have a relationship with the lender for many years. |
Use specialized calculators to compare multiple loan offers side by side, considering all costs and benefits. These tools help you visualize the long-term impact of different offers.
Create a structured comparison chart to evaluate multiple loan offers against your specific priorities and requirements.
Conduct a detailed analysis of both immediate and long-term costs against benefits for each loan option, considering your specific financial situation.
Seek advice from financial advisors or loan consultants like Arav Digital Fincare who can provide personalized recommendations based on their expertise and market knowledge.
Before comparing offers, determine what matters most to you—lowest EMI, lowest total interest, flexible prepayment options, quick disbursement, or service quality.
Don't focus solely on the advertised interest rate. Consider the APR, processing fees, and other charges that contribute to the total cost of the loan.
Ask for complete amortization schedules from each lender to understand how your payments will be distributed between principal and interest over time.
Scrutinize the terms and conditions, focusing on prepayment penalties, default consequences, and any hidden charges not explicitly mentioned.
Use competing offers as leverage to negotiate better terms with your preferred lender. Many terms, including interest rates and processing fees, can be negotiable.
At Arav Digital Fincare, we simplify the loan comparison process by presenting offers from multiple banks side by side, highlighting the pros and cons of each option based on your specific requirements.
Compare Loan OffersYour credit score plays a crucial role in loan approval, interest rates, and overall borrowing capacity. Understanding and maintaining a good credit score is essential for financial success.
In India, credit scores (primarily CIBIL) range from 300 to 900, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. Here's what different score ranges typically indicate:
Significant credit issues, high rejection probability
Below average, possible approval with higher rates
Above average, decent approval chances
Very good credit, best rates and terms
| Credit Score Range | Loan Approval | Interest Rate Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 750-900 | Highest approval rates | Best rates (1-2% lower than average) |
| 700-749 | Good approval chances | Competitive rates (0.5-1% lower) |
| 650-699 | Moderate approval chances | Average market rates |
| 600-649 | Lower approval chances | Higher rates (1-2% above average) |
| Below 600 | Very low approval rates | Significantly higher rates (3%+ above average) or rejection |
Your credit score is calculated based on several key factors. Understanding these can help you maintain or improve your score:
Your track record of paying bills and EMIs on time. Late payments, defaults, and settlements negatively impact this factor.
The percentage of available credit you're using. Keeping utilization below 30% of your total available credit is optimal.
The duration for which you've had credit accounts. Longer history generally results in higher scores.